Subdivision of Journal:
Definition of Subdivision:
In a
large business concern a journal is divided into
parts so that several clerk could work at the same
time. This is known as subdivision of journal.
Purpose of Subdivision:
In
small concerns only one journal and one ledger may
serve the purpose, because the number of
transactions is very small. But in large business
concerns the number of transactions are numerous,
just one journal and one ledger will not do the job.
That will cause much inconvenience i.e., if we have
only one journal in a large scale business, it is
not possible for one bookkeeper to record all the
transactions in time. On the other hand, it will not
be possible for more than one person to use the same
journal simultaneously with the result that the
accounting work will fall in arrear.
There
are some more factors which necessitate the use of
more than one subsidiary book (journal):
-
If
all the transactions are recorded in one book
(journal), the book will be very large, bulky,
and difficult to handle.
-
If one
bookkeeper is asked to record all the transactions,
the possibility of errors and mistakes will be
great. It will also create opportunities for
committing fraud.
-
If all
the transactions are recorded in one book, it will
be difficult to trace out a particular transaction
in future.
How Many Journals A Business Should
Have?
We know
that different types of transactions take place in a
business concern. Some transactions take place
repeatedly (hundreds to thousands times in a year) and
some transactions take place once or twice in a year.
Obviously, it is not logical to provide a separate
journal for transactions which rarely take place.
For this
purpose different groups of transactions are made and a
separate book is provided for each group. Each group is
consisted of similar types of transactions. Journal is
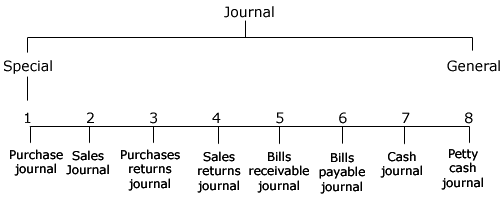
mainly divided into two:
-
Special journal
-
General
journal
Special Journal:
By special
journal we mean, a journal in which transactions relating to
a certain special group or recorded. Special journal is
again subdivided into eight groups:
-
Purchases
book or purchases journal
-
Sales book or
sales journal
-
Purchases returns
book or purchases returns journal
-
Sales returns book
or sales returns journal
-
Bills receivable book
-
Bills payable book
-
Cash book or cash journal
-
Petty cash book
General Journal:
The transactions which do not fall
with in the scope of above mentioned books, are recorded in this journal e.g.
purchase of an asset on credit, depreciation on assets, expenses payable, bad
debts etc. It is also known as journal proper, Modern journal or principle
journal. Some authors call it only "journal".
The main function of the above
books is to supply necessary information to the ledger. All the transactions are
posted in the ledger on the basis of information available from these books, so
these books are called subsidiary books
Advantages of Subdivision of Journal:
The following advantages are
derived from division of journal:
-
Because of subdivision the
books cannot be bulky and hence there will be no difficulty in handling
them.
-
Accounting work is divided amongst
a large number of employees. So work is done nicely and promptly and no work is
left in arrear.
-
Each employee can be held
responsible for mistakes committed by him. This serves as caution and care to
the employees.
-
The efficiency of the
employees increases because of the division of labor.
-
By keeping the book under the
custody of different employees the chances of fraud and defalcation are
minimized.
Relevant Articles:
|